Overview of Triggers
A database trigger is a stored procedure associated with a database table, view, or event. The trigger can be called once, when some event occurs, or many times, once for each row affected by anINSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE
statement. The trigger can be called after the event, to record it, or
take some follow-up action. The trigger can be called before the event,
to prevent erroneous operations or fix new data so that it conforms to
business rules. The executable part of a trigger can contain procedural
statements and SQL data manipulation statements.Triggers are created using the SQL
CREATE TRIGGER statement. This statement can be used with Object Browser, SQL Script Editor, or SQL Command Line (SQL*Plus). The CREATE (or CREATE OR REPLACE) statement fails if any errors exist in the PL/SQL block.This section contains the following topics:
-
Types of Triggers
-
Naming Triggers
-
When Is a Trigger Fired?
-
Controlling When a Trigger Is Fired
-
Accessing Column Values in Row Triggers
-
Detecting the DML Operation That Fired a Trigger
-
Enabled and Disabled Trigger Modes
-
Error Conditions and Exceptions in the Trigger Body
Types of Triggers
A trigger can be a stored PL/SQL or C procedure associated with a table, view, schema, or the database itself. Oracle Database XE automatically executes a trigger when a specified event takes place, which usually is a DML statement being issued against the table. The types of triggers are:
-
DML triggers on tables
-
INSTEADOFtriggers on views
-
System triggers on
DATABASEorSCHEMA
-
DML statements (
DELETE,INSERT,UPDATE)
-
DDL statements (
CREATE,ALTER,DROP)
-
Database operations (
LOGON,LOGOFF)
Naming Triggers
Trigger names must be unique with respect to other triggers in the same schema. Trigger names do not need to be unique with respect to other schema objects, such as tables, views, and procedures. For example, a table and a trigger can have the same name; however, to avoid confusion, this is not recommended.
When Is a Trigger Fired?
A trigger is fired based on a triggering statement, which specifies:
-
The SQL statement or the system event, database event, or DDL event that fires the trigger body. The options include
DELETE,INSERT, andUPDATE. One, two, or all three of these options can be included in the triggering statement specification.
-
The table, view, database, or schema associated with the trigger.
AFTER DELETE OR INSERT OR UPDATE ON employees ...
then any of the following statements would fire the trigger:
DELETE FROM employees WHERE ...;
INSERT INTO employees VALUES ( ... );
INSERT INTO employees SELECT ... FROM ... ;
UPDATE employees SET ... ;
AnUPDATEstatement might include a list of columns. If a triggering statement includes a column list, the trigger is fired only when one of the specified columns is updated. If a triggering statement omits a column list, the trigger is fired when any column of the associated table is updated. A column list cannot be specified forINSERTorDELETEtriggering statements. In Example 6-1 theaudit_saltrigger specifies thesalarycolumn, and is only fired after anUPDATEof the salary of an employee in theemployeestable. Updates of other columns would not fire the trigger.
Controlling When a Trigger Is Fired
This section describes options that control when a trigger is fired.
This section contains the following topics:
-
Firing Triggers With the BEORE and AFTER Options
-
Firing Triggers With the FOR EACH ROW Option
-
Firing Triggers Based on Conditions (WHEN Clause)
-
Firing Triggers With the INSTEAD OF Option
Firing Triggers With the BEORE and AFTER Options
TheBEFOREorAFTERoption in theCREATETRIGGERstatement specifies exactly when to fire the trigger body in relation to the triggering statement that is being run. In aCREATETRIGGERstatement, theBEFOREorAFTERoption is specified just before the triggering statement.
In general, you useBEFOREorAFTERtriggers to achieve the following results:
-
Use a
BEFORErow trigger to modify the row before the row data is written to disk. See Example 6-2 for an example of aBEFOREtrigger.
-
Use an
AFTERrow trigger to obtain and perform operations using the row ID. See Example 6-1 for an example of anAFTERtrigger.
Note:BEFORErow triggers are slightly more efficient thanAFTERrow triggers. WithAFTERrow triggers, affected data blocks must be read (logical read, not physical read) once for the trigger and then again for the triggering statement. Alternatively, withBEFORErow triggers, the data blocks must be read only once for both the triggering statement and the trigger.
UPDATEorDELETEstatement detects a conflict with a concurrentUPDATEstatement, then Oracle Database XE performs a transparentROLLBACKand restarts the update operation. This can occur many times before the statement completes successfully. Each time the statement is restarted, theBEFOREstatement trigger is fired again. The rollback does not undo changes to any package variables referenced in the trigger. Your package should include a counter variable to detect this situation.
Firing Triggers With the FOR EACH ROW Option
TheFOREACHROWoption determines whether the trigger is a row trigger or a statement trigger. If you specifyFOREACHROW, then the trigger fires once for each row of the table that is affected by the triggering statement. These triggers are referred to as row-level triggers. See the use ofFOREACHROWin Example 6-1 and Example 6-2.
The absence of theFOREACHROWoption indicates that the trigger fires only once for each applicable statement, but not separately for each row affected by the statement. These triggers are referred to as statement-level triggers and are useful for performing validation checks for the entire statement. In Example 6-6, the trigger fires only once for each update of theemployeestable.
Firing Triggers Based on Conditions (WHEN Clause)
An optional trigger restriction can be included in the definition of a row trigger by specifying a Boolean SQL expression in aWHENclause.
If included, the expression in theWHENclause is evaluated for each row that the trigger affects. If the expression evaluates toTRUEfor a row, then the trigger body is fired on behalf of that row. Otherwise, if the expression evaluates toFALSE, the trigger body is not fired. See Example 6-2 for an example of the use of theWHENclause in a trigger.
The expression in aWHENclause must be a SQL expression, and it cannot include a subquery. You cannot use a PL/SQL expression (including user-defined functions) in aWHENclause. AWHENclause cannot be included in the definition of a statement trigger.
Firing Triggers With the INSTEAD OF Option
Use theINSTEADOFoption to fire the trigger instead of executing the triggering event. Unlike other types of triggers, Oracle Database XE fires the trigger instead of executing the triggering SQL DML statement.
With anINSTEADOFtrigger, you can run anUPDATE,INSERT, orDELETEstatement on a complex view that otherwise could not be updated. Also, the trigger can be used to control how updates are performed on a view. TheINSTEADOFtrigger runs transparently in the background to perform the correct actions on the underlying tables of the view. TheINSTEADOFoption only can only be specified for a trigger created on a view and can only be activated for each row.INSTEADOFtriggers are valid for DML events on views. They are not valid for DDL or database events.
See "Creating a Trigger With the INSTEAD OF Option".
Accessing Column Values in Row Triggers
Within a trigger body of a row trigger, the PL/SQL code and SQL statements have access to the old and new column values of the current row affected by the triggering statement. Two correlation names exist for every column of the table being modified. There is one for the old column value and one for the new column value. These columns in the table are identified by:OLD.colum_nameand:NEW.column_name. The use of:NEWand:OLDis shown in Example 6-1 and Example 6-2.
Depending on the type of triggering statement, certain correlation names might not have any meaning:
-
A trigger fired by an
INSERTstatement has meaningful access to new column values only. Because the row is being created by theINSERToperation, the old values are null.
-
A trigger fired by an
UPDATEstatement has access to both old and new column values for bothBEFOREandAFTERrow triggers.
-
A trigger fired by a
DELETEstatement has meaningful access to old (:OLD) column values only. Because the row no longer exists after the row is deleted, the new (:NEW) values areNULLand cannot be modified.
BEFOREandAFTERrow triggers. Anewcolumn value can be assigned in aBEFORErow trigger, but not in anAFTERrow trigger (because the triggering statement takes effect before anAFTERrow trigger is fired). If aBEFORErow trigger changes the value ofNEW.column, then anAFTERrow trigger fired by the same statement sees the change assigned by theBEFORErow trigger.
Correlation names can also be used in the Boolean expression of aWHENclause. A colon (:) must precede theOLDandNEWqualifiers when they are used in a trigger body, but a colon is not allowed when using the qualifiers in theWHENclause.
Detecting the DML Operation That Fired a Trigger
If more than one type of DML operation can fire a trigger, such asONINSERTorUPDATE, the trigger body can use the conditional predicatesINSERTING,DELETING, andUPDATINGto check which type of statement fires the trigger.
Within the code of the trigger body, you can execute blocks of code depending on the kind of DML operation that fired the trigger. For an example ofINSERTINGandUPDATINGpredicates, see Example 6-6.
In anUPDATEtrigger, a column name can be specified with anUPDATINGconditional predicate to determine if the named column is being updated. For example, assume a trigger is defined as the following:
CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER ...
... UPDATE OF salary ON employees ...
BEGIN
... IF UPDATING ('salary') THEN ... END IF;
...
The code in theTHENclause runs only if the triggeringUPDATEstatement updates thesalarycolumn. This way, the trigger can minimize its overhead when the column of interest is not being changed.
Enabled and Disabled Trigger Modes
This section discusses enabled and disabled triggers. A trigger can be in an enabled or disabled mode:
-
An
enabled trigger executes its trigger body if a triggering statement is
entered and the trigger restriction (if any) evaluates to
TRUE.
-
A
disabled trigger does not execute its trigger body, even if a
triggering statement is entered and the trigger restriction (if any)
evaluates to
TRUE.
See "Enabling Triggers" and "Disabling Triggers".
Error Conditions and Exceptions in the Trigger Body
If a predefined or user-defined error condition or exception occurs during the execution of a trigger body, then all effects of the trigger body, as well as the triggering statement, are rolled back unless the error is trapped by an exception handler. Therefore, a trigger body can prevent the execution of the triggering statement by raising an exception. User-defined exceptions are commonly used in triggers that enforce complex security authorizations or integrity constraints. See "Creating a Trigger With an Exception Handler" and "Handling PL/SQL Errors".
Designing Triggers
This section discusses the design of triggers.
This section contains the following topics:
Guidelines For Triggers
Use the following guidelines when designing triggers:
-
Use triggers to guarantee that when a specific operation is performed, related actions are performed.
-
Do not define triggers that duplicate features already built into
Oracle Database XE. For example, do not define triggers to reject bad
data if you can do the same checking through declarative integrity
constraints.
-
Limit the size of triggers. If the logic for a trigger requires more
than 60 lines of PL/SQL code, it is better to include most of the code
in a stored procedure, and call the procedure from the trigger. The size
of the trigger cannot be more than 32K.
-
Use triggers only for centralized, global operations that should be
fired for the triggering statement, regardless of which user or database
application issues the statement.
-
Do not create recursive triggers. For example, creating an
AFTERUPDATEstatement trigger on theemployeestable that will then issue anUPDATEstatement on the sameemployeestable, will cause the trigger to fire recursively until it has run out of memory.
-
Use triggers on the database judiciously. They are executed for every
user, every time the event occurs on which the trigger is created.
Restrictions For Creating Triggers
When creating triggers with PL/SQL code, there are some restrictions that are not required for standard PL/SQL blocks. The following sections discuss these restrictions.
SQL Statements Allowed in Trigger BodiesThe body of a trigger can contain DML SQL statements. It can also containSELECTstatements, but they must beSELECT...INTO... statements or theSELECTstatement in the definition of a cursor.
DDL statements are not allowed in the body of a trigger and transaction control statements are not allowed in a trigger.ROLLBACK,COMMIT, andSAVEPOINTstatements cannot be used. For system triggers,CREATE,ALTER, andDROPTABLEstatements andALTER...COMPILEstatements are allowed.
Statements inside of a trigger can reference remote schema objects. However, pay special attention when calling remote procedures from within a local trigger. If a timestamp or signature mismatch is found during execution of the trigger, then the remote procedure is not run, and the trigger is invalidated.Note:A procedure called by a trigger cannot run the previous transaction control statements because the procedure runs within the context of the trigger body.
Only committed triggers are fired. For example, if you create a trigger that should be fired after allCREATEevents, then the trigger itself does not fire after the creation, because the correct information about this trigger was not committed at the time when the trigger onCREATEevents was fired.
For example, if you execute the following SQL statement, triggermy_triggeris not fired after the creation ofmy_trigger. Oracle Database XE does not fire a trigger that is not committed.
CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER my_trigger
AFTER CREATE ON DATABASE
BEGIN
NULL;
END;Privileges Needed to Work with Triggers
To create a trigger in your schema, you must have theCREATETRIGGERsystem privilege, and one of the following:
-
Own the table specified in the triggering statement
-
Have the
ALTERprivilege for the table in the triggering statement
-
Have the
ALTERANYTABLEsystem privilege
CREATETRIGGERsystem privilege is included in predefinedRESOURCErole that has been granted to the userHR. See "Logging in to the Database Home Page".
To create a trigger on a database, you must have theADMINISTERDATABASETRIGGERprivilege. If this privilege is later revoked, then you can drop the trigger, but not alter it.
The object privileges to the schema objects referenced in the trigger body must be granted to the trigger owner explicitly (not through a role). The statements in the trigger body operate under the privilege domain of the trigger owner, not the privilege domain of the user issuing the triggering statement. This is similar to the privilege model for stored procedures.
Managing Triggers in the Database
Triggers are another type of database object that you can manage with Object Browser. You can also create and update triggers with the SQL Commands page or SQL Editor page.
In addition, you can use SQL Command Line (SQL*Plus) to create and update triggers. For information about using SQL Command Line, see Appendix A, "Using SQL Command Line".
-
DML triggers on tables
-
Creating a Trigger With the SQL Commands Page
-
Creating a Trigger With the Object Browser Page
-
Viewing a Trigger With Object Browser
-
Creating a Trigger With the AFTER and FOR EACH ROW Option
-
Creating a Trigger With the BEFORE Option and WHEN Clause
-
Creating a Trigger With the INSTEAD OF Option
-
Creating a Trigger With an Exception Handler
-
Creating a Trigger That Fires Once For Each Update
-
Creating LOGON and LOGOFF Triggers
-
Modifying Triggers
-
Dropping Triggers
-
Disabling Triggers
-
Enabling Triggers
-
Compiling Triggers
See Also:
Oracle Database Application Developer's Guide - Fundamentals for information about the uses for and creation of triggersCreating a Trigger With the SQL Commands Page
With the SQL Commands page, you can create and update triggers.To create a trigger with the SQL Commands page:
-
Log in to the Database Home Page. See "Logging in to the Database Home Page". To run the examples in this guide, you should log in as user
HRwith your password for theHRaccount.
-
On the home page, click the SQL icon to display the SQL page.
-
Click the SQL Commands icon to display the SQL Command page.
-
On the SQL Commands page, first enter the SQL statements to create
any objects that are needed in the trigger body. For example, the
emp_audittable needs to be created before creating theaudit_saltrigger in Example 6-1. If a database object is referred to in the trigger code, then that object must exist for the trigger to be valid.
-
Click the Run button to execute the SQL
statements to create any supporting objects for the trigger. If the
statements run successfully, delete the statements from the SQL Commands
page. Otherwise, update the statements so they run successfully.
-
On the SQL Commands page, enter the PL/SQL code to create the trigger
after any objects that are needed by the trigger are created. For an
example of code to create a trigger, see Example 6-1.
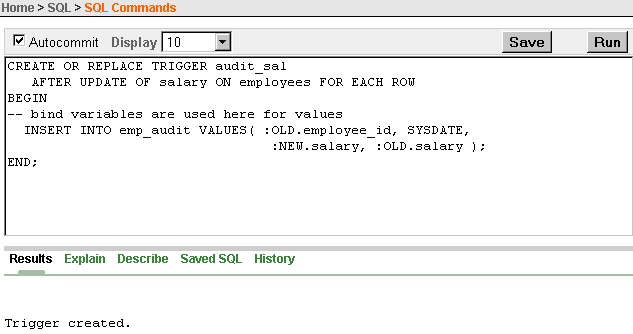
Description of the illustration xe_create_trigger_sql.gif
-
Click the Run button to execute the PL/SQL code to create the trigger. Correct the code if it does not execute successfully.
-
If you want to save the PL/SQL code for future use, click the Save button.
-
In the Name field, enter a name for the saved PL/SQL code. You can also enter an optional description. Click the Save button to complete the action.
-
To access the saved PL/SQL code, click the Saved SQL tab and select the name of the saved PL/SQL code that you want to access.
See Also:
Oracle Database Express Edition Application Express User's Guide for detailed information about using SQL CommandsCreating a Trigger With the Object Browser Page
You can create and update triggers in the database with Object Browser.To create a trigger with the Object Browser page:
-
Log in to the Database Home Page. See "Logging in to the Database Home Page". To run the examples in this guide, log in as user
HRwith your password for theHRaccount.
-
Click the Object Browser icon on the Database Home Page.
-
Click the Create button, and select Trigger from the list.
-
Enter the name of the table (
employees) that the trigger activity is based on and click the Next button. You can also select a table name from list.
-
In the Trigger Name field, enter the trigger name (
emp_salary_trigger). The the Preserve Case box should be unchecked.
-
From the Firing Point list, select the firing point (
AFTER).
-
From the Options list, select an option (
updateof).
-
From the Column list, select a column (salary).
-
Check the For Each Row option. Do not enter anything in the When field.
-
In the Trigger Body field, enter the code for the trigger body. See Example 6-1.
Note that if a database object is referred to in the trigger body code,
then that object must exist for the trigger to be valid.
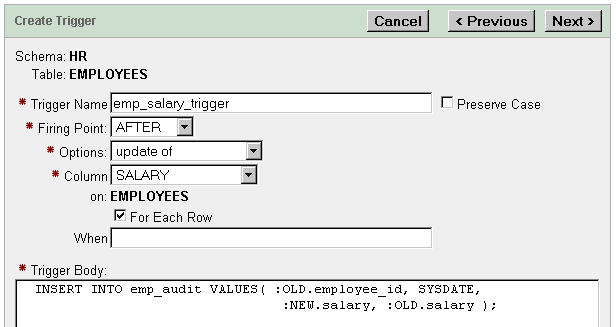
Description of the illustration xe_create_trigger.gif
-
Click the Next button.
-
Click the SQL button to view the SQL statements for creating the trigger.
-
Click the Finish button to complete the action.
See Also:
Oracle Database Express Edition Application Express User's Guide for information about managing triggers with the Object Browser pageViewing a Trigger With Object Browser
To find out which triggers exist in your database and display information about a specific trigger, use the Object Browser.To display information about a trigger with Object Browser:
-
Log in to the Database Home Page. See "Logging in to the Database Home Page".
-
Click the Object Browser icon on the Database Home Page.
-
Select Triggers in the object list, then select the trigger (
emp_salary_trigger) you want to display.
-
Click the Object Details tab to display details about the trigger.
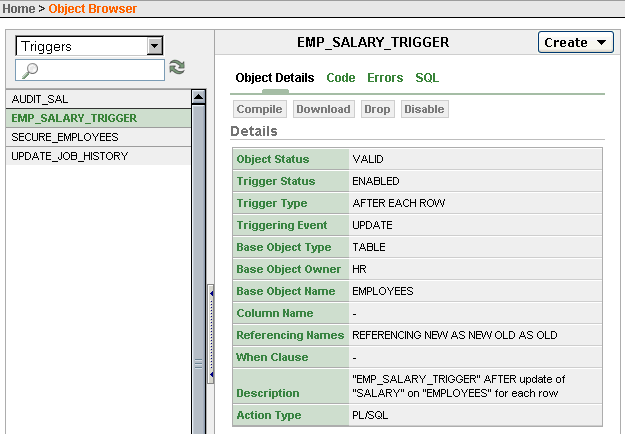
Description of the illustration xe_view_triggers.gif
-
Click the Code, Errors, or SQL tab to display additional information about the trigger.
HR.update_job_history trigger is fired whenever an update is performed on the department_id or job_id column of an employee record. This trigger writes a record to the job_history table and can raise an error if more than one update occurs in a single day.Creating a Trigger With the AFTER and FOR EACH ROW Option
Example 6-1 shows the code for a trigger on theemployees table. In the example, the table-level trigger fires after salaries in the employees table are updated and writes a record in an audit table.With the
FOR EACH ROW option, the trigger writes a record to the emp_audit
table for each update. This record contains the employee ID, the date
of the update, the updated salary, and the original salary. Note the use
of the :OLD.column_name and :NEW.column_name to access the values in the columns before and after the update.With the
AFTER keyword, the trigger can also query or
change the same table. Triggers can only do that after the initial
changes are applied, and the table is back in a consistent state.Because the trigger uses the
FOR EACH ROW
clause, it might be executed multiple times, such as when updating or
deleting multiple rows. You might omit this clause if you just want to
record the fact that the operation occurred, but not examine the data
for each row.
Example 6-1 Creating a Database Trigger WIth the AFTER Option
-- create a table to use for with the trigger in this example if
-- it has not already been created previously
-- if the table does not exist, the trigger will be invalid
CREATE TABLE emp_audit ( emp_audit_id NUMBER(6), up_date DATE,
new_sal NUMBER(8,2), old_sal NUMBER(8,2) );
-- create or replace the trigger
CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER audit_sal
AFTER UPDATE OF salary ON employees FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
-- bind variables are used here for values
INSERT INTO emp_audit VALUES( :OLD.employee_id, SYSDATE,
:NEW.salary, :OLD.salary );
END;
/
-- fire the trigger with an update of salary
UPDATE employees SET salary = salary * 1.01 WHERE manager_id = 122;
-- check the audit table to see if trigger was fired
SELECT * FROM emp_audit;
Creating a Trigger With the BEFORE Option and WHEN Clause
In Example 6-2, you define aBEFORE
trigger that is fired for each row that is updated. If there are five
employees in department 20, and the salaries for all the employees in
the department are updated, then the trigger fires five times when those
rows are updated. Note the use of the WHEN clause to restrict the firing of the trigger.
Example 6-2 Creating a Database Trigger With the BEFORE Option
-- create a temporary table
CREATE TABLE emp_sal_log (emp_id NUMBER, log_date DATE,
new_salary NUMBER, action VARCHAR2(50));
CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER log_salary_increase -- create a trigger
BEFORE UPDATE of salary ON employees FOR EACH ROW
WHEN (OLD.salary < 8000)
BEGIN
INSERT INTO emp_sal_log (emp_id, log_date, new_salary, action)
VALUES (:NEW.employee_id, SYSDATE, :NEW.salary, 'New Salary');
END;
/
-- update the salary with the following UPDATE statement
-- trigger fires for each row that is udpated
UPDATE employees SET salary = salary * 1.01 WHERE department_id = 60;
-- view the log table
SELECT * FROM emp_sal_log;
Creating a Trigger With the INSTEAD OF Option
In Example 6-3 a view is created with multiple underlying tables. Note that the view in the example uses theJOIN syntax to display data from multiple tables. See "Displaying Data From Multiple Tables".
Example 6-3 Creating a View That is Updated With an INSTEAD OF Trigger
CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW my_mgr_view AS SELECT ( d.department_id || ' ' || d.department_name) "Department", d.manager_id, e.first_name, e.last_name, e.email, e.hire_date "Hired On", e.phone_number, e.salary, e.commission_pct, (e.job_id || ' ' || j.job_title) "Job Class" FROM departments d JOIN employees e ON d.manager_id = e.employee_id JOIN jobs j ON e.job_id = j.job_id ORDER BY d.department_id;
first_name, last_name, email, phone_number, salary, or commission_pct) in the view in Example 6-3 with a SQL UPDATE statement. For example, the employees table cannot be updated with an UPDATE statement such as:UPDATE my_mgr_view SET first_name = 'Denis' WHERE manager_id = 114;-- using WHERE employee_id = 114 does not work alsoIn Example 6-4 an
INSTEAD OF trigger is created that updates the underlying employees table of the view when an UPDATE statement is run on the view.
Example 6-4 Creating an INSTEAD OF Trigger for Updating a View
CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER update_my_mgr_view INSTEAD OF UPDATE ON my_mgr_view FOR EACH ROW BEGIN -- allow the following updates to the underlying employees table UPDATE employees SET last_name = :NEW.last_name, first_name = :NEW.first_name, email = :NEW.email, phone_number = :NEW.phone_number, salary = :NEW.salary, commission_pct = :NEW.commission_pct WHERE employee_id = :OLD.manager_id; END; /
UPDATE statement can be run on the view and the INSTEAD OF trigger performs the update.UPDATE my_mgr_view SET first_name = 'Denis' WHERE manager_id = 114;
Creating a Trigger With an Exception Handler
Example 6-5 shows how to include an exception handler with a trigger. In this example, an exception is raised if anUPDATE operation changes the manager ID of an employee.
Example 6-5 Creating a Database Trigger With an Exception Handler
-- create a temporary table
CREATE TABLE emp_except_log (emp_id NUMBER, mgr_id_new NUMBER,
mgr_id_old NUMBER, log_date DATE, action VARCHAR2(50));
CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER emp_log_update -- create a trigger
BEFORE UPDATE ON employees FOR EACH ROW
DECLARE
mgrid_exception EXCEPTION;
BEGIN
IF (:NEW.manager_id <> :OLD.manager_id) THEN
RAISE mgrid_exception;
END IF;
INSERT INTO emp_except_log (emp_id, mgr_id_new, mgr_id_old, log_date, action)
VALUES (:NEW.employee_id, :NEW.manager_id, :OLD.manager_id,
SYSDATE, 'Employee updated');
EXCEPTION
WHEN mgrid_exception THEN
INSERT INTO emp_except_log (emp_id, mgr_id_new, mgr_id_old, log_date, action)
VALUES (:NEW.employee_id, :NEW.manager_id, :OLD.manager_id,
SYSDATE, 'Employee manager ID updated!');
END;
/
-- update employees with the following UPDATE statements, firing trigger
UPDATE employees SET salary = salary * 1.01 WHERE employee_id = 105;
-- the trigger raises an exception with this UPDATE
UPDATE employees SET manager_id = 102 WHERE employee_id = 105;
-- view the log table
SELECT * FROM emp_except_log;
Creating a Trigger That Fires Once For Each Update
In Example 6-6, theFOR EACH ROW clause is omitted so the trigger fires only once for each update of or insert into the employees table. Because there are two operations that fire the trigger, this example includes IF-THEN statements to log the specific operation that fired the trigger. The check for the INSERTING condition evaluates to TRUE only if the statement that fired the trigger is an INSERT statement. The check for the UPDATING condition evaluates to TRUE only if the statement that fired the trigger is an UPDATE statement.
Example 6-6 Creating a Trigger That Fires Only Once
-- create a log table
CREATE TABLE emp_update_log (log_date DATE, action VARCHAR2(50));
-- create a trigger
CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER log_emp_update
AFTER UPDATE OR INSERT ON employees
DECLARE
v_action VARCHAR2(50);
BEGIN
IF UPDATING THEN
v_action := 'A row has been updated in the employees table';
END IF;
IF INSERTING THEN
v_action := 'A row has been inserted in the employees table';
END IF;
INSERT INTO emp_update_log (log_date, action)
VALUES (SYSDATE, v_action);
END;
/
-- fire the trigger with an update
UPDATE employees SET salary = salary * 1.01 WHERE department_id = 60;
INSERT INTO employees VALUES(14, 'Belden', 'Enrique', 'EBELDEN','555.111.2222',
'31-AUG-05', 'AC_MGR', 9000, .1, 101, 110);
-- view the log table
SELECT * FROM emp_update_log;
-- clean up: remove the inserted record
DELETE FROM employees WHERE employee_id = 14;
Creating LOGON and LOGOFF Triggers
You can create a trigger that performs an action when a user logs on or off the database.In Example 6-7, a trigger is created to write a record to a log table whenever a user logs on to the
HR account. In this example, the user name (USER), the type of activity (LOGON or LOGOFF), current system date (SYSDATE), and the number of employees in the employees table are written to a table. Both SYSDATE and USER are pseudocolumns that return values. See "Using ROWNUM, SYSDATE, and USER Pseudocolumns With SQL".
Example 6-7 Creating a LOGON Trigger
-- create a table to hold the data on user logons and logoffs
CREATE TABLE hr_log_table ( user_name VARCHAR2(30), activity VARCHAR2(20),
logon_date DATE, employee_count NUMBER );
-- create a trigger that inserts a record in hr_log_table
-- every time a user logs on to the HR schema
CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER on_hr_logon
AFTER LOGON
ON HR.schema
DECLARE
emp_count NUMBER;
BEGIN
SELECT COUNT(*) INTO emp_count FROM employees; -- count the number of employees
INSERT INTO hr_log_table VALUES(USER, 'Log on', SYSDATE, emp_count);
END;
/
HR account.
Example 6-8 Creating a LOGOFF Trigger
-- create a trigger that inserts a record in hr_log_table -- every time a user logs off the HR schema CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER on_hr_logoff BEFORE LOGOFF ON HR.schema DECLARE emp_count NUMBER; BEGIN SELECT COUNT(*) INTO emp_count FROM employees; -- count the number of employees INSERT INTO hr_log_table VALUES(USER, 'Log off', SYSDATE, emp_count); END; /
HR account, you can check the hr_log_table to view results of the triggers. For example:DISCONNECT CONNECT hr/hr SELECT * FROM hr_log_table;
Modifying Triggers
Similar to a stored procedure, a trigger cannot be explicitly altered. It must be replaced with a new definition. TheALTER TRIGGER statement is used only to recompile, enable, or disable a trigger.When replacing a trigger, you must include the
OR REPLACE option in the CREATE TRIGGER statement. The OR REPLACE
option is provided to allow a new version of an existing trigger to
replace the older version, without affecting any grants made for the
original version of the trigger.Alternatively, the trigger can be dropped using the
DROP TRIGGER statement, and you can rerun the CREATE TRIGGER statement. To drop a trigger, the trigger must be in your schema, or you must have the
DROP ANY TRIGGER system privilege.Dropping Triggers
When you no longer need a trigger, you can drop the trigger with Object Browser or with the SQLDROP command. After dropping a trigger, you can drop any dependent objects that are no longer needed.You can disable, rather than drop, a trigger if you temporarily want to stop it from firing. See Disabling Triggers.
Example 6-9 shows how to drop triggers and tables used by the triggers.
Example 6-9 Dropping Triggers
-- first, drop the audit_sal trigger DROP TRIGGER audit_sal; -- then drop the table used by the trigger DROP TABLE emp_audit; -- drop the log_salary_increase trigger, then the table used by the trigger DROP TRIGGER log_salary_increase; DROP TABLE emp_sal_log; -- drop the emp_log_update trigger, then the table used by the trigger DROP TRIGGER emp_log_update; DROP TABLE emp_except_log; -- drop on_hr_logoff and on_hr_logon triggers, then drop hr_log_table DROP TRIGGER on_hr_logon; DROP TRIGGER on_hr_logoff; DROP TABLE hr_log_table;
Disabling Triggers
You can temporarily disable a trigger. You might want to do this if:-
An object it references is not available.
-
You need to perform a large data load, and you want it to proceed quickly without firing triggers.
-
You are reloading data.
ALTER TRIGGER statement with the DISABLE option as shown in Example 6-10.All triggers associated with a table can be disabled with one statement using the
ALTER TABLE statement with the DISABLE clause and the ALL TRIGGERS option. Example 6-11 shows how to disable all triggers defined for the departments table.Enabling Triggers
By default, a trigger is automatically enabled when it is created. However, it can be disabled if necessary. After you complete the task that requires the trigger to be disabled, reenable the trigger so that it fires when appropriate.To enable a disabled trigger, use the
ALTER TRIGGER statement with the ENABLE option as shown in Example 6-12.All triggers defined for a specific table can be enabled with one statement using the
ALTER TABLE statement with the ENABLE clause with the ALL TRIGGERS option. Example 6-13 shows how to enable all triggers defined for the departments table.Compiling Triggers
Triggers are similar to PL/SQL anonymous blocks with the addition of the :NEW and :OLD
capabilities, but their compilation is different. A PL/SQL anonymous
block is compiled each time it is loaded into memory. Triggers, in
contrast, are fully compiled when the CREATE TRIGGER statement is entered, and the code is stored in the data dictionary. This means that a trigger is executed directly.This section contains the following topics:
Trigger Errors
If errors occur during the compilation of a trigger, then the trigger is still created. If a DML statement fires this trigger, then the DML statement fails. You can use theSHOW ERRORS statement in SQL Command Line to display any compilation errors when you create a trigger in SQL, or you can use the SELECT statement to display the errors from the USER_ERRORS view as follows:SELECT * FROM USER_ERRORS WHERE TYPE = 'TRIGGER';
Dependencies for Triggers
Compiled triggers have dependencies on database objects and become invalid if these objects, such as a table accessed from or a stored procedure called from the trigger body, is modified. Triggers that are invalidated for dependency reasons are recompiled the next time they are invoked.You can examine the
ALL_DEPENDENCIES view to see the dependencies for a trigger. Example 6-14 shows the use of the SQL SELECT statement to display the dependencies for a trigger in the HR schema.
Example 6-14 Viewing the Dependencies for a Trigger
SELECT NAME, REFERENCED_OWNER, REFERENCED_NAME, REFERENCED_TYPE
FROM ALL_DEPENDENCIES
WHERE OWNER = 'HR' and TYPE = 'TRIGGER' AND NAME = 'LOG_EMP_UPDATE';
Triggers can depend on other functions, procedures, or packages. If the function, procedure, or package specified in the trigger is dropped, then the trigger is marked invalid. An attempt is made to validate the trigger when the event occurs. If the trigger cannot be validated successfully, then it is marked
VALID WITH ERRORS, and the event fails. For information about viewing invalid triggers in a database, see "Viewing Information With Object Reports".
Note:
There is an exception for STARTUP events. STARTUP events succeed even if the trigger fails. There are also exceptions for SHUTDOWN events and for LOGON events if you login as SYSTEM.Recompiling Triggers
Use theALTER TRIGGER statement to recompile a trigger manually. Example 6-15 shows the use of the SQL ALTER TRIGGER statement to recompile the emp_log_update trigger.
Example 6-15 Recompiling a Trigger
ALTER TRIGGER log_emp_update COMPILE; -- cleanup: drop the log_emp_update trigger and emp_update_log table DROP TRIGGER log_emp_update; DROP TABLE emp_update_log;
I loved your post.Much thanks again. Fantastic.
ReplyDeleteweb methods training
web methods online training