Chart of Accounts Implementation in Oracle Apps R12 (Part 1)
Definition from Wikipedia:
Chart
of accounts (COA) is a list of the accounts used by an organization.
The list can be numerical, alphabetic, or alpha-numeric. The structure
and headings of accounts should assist in consistent posting of
transactions. Each nominal ledger account is unique to allow its ledger
to be located. The list is typically arranged in the order of the
customary appearance of accounts in the financial statements, profit and
loss accounts followed by balance sheet accounts.
Overview:
This
post will introduce the process flow for creating a chart of accounts.
The chart of Accounts defines the accounting structure of the
organization. This structure includes every aspects of the business like
business units, accounts, products, services, geographical locations
etc. Further COA also tells us about how the elements of the structure
combined to form the account combination.
Uses:
- Accounting combinations defined in Chart of Accounts is used to various transactions happening in the organization.
- Helps in generating account balances.
- Helps in Reporting
- Helps in Analyzing financial information
- Many more …
Basic Steps Involved in Implementation:
Chart of Accounts Implementation in Oracle Apps R12 (Part 2)
:
STEPS IN DETAIL:
1. Value Set Definition:
The
value set is the group of values that determine the attributes of the
segment. The definition of value set decides whether the value entered
for the corresponding segment is acceptable or not. We have to define
the value sets for each segment we planned to have in Account
combination.
Navigation: General Ledger Super User Responsibility
Setup à Financials à
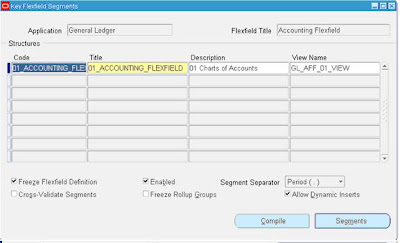
2. Defining Accounting Flexifield Structure
Define an accounting flexfield structure using the Key Flexfield Segments form.
Caution 1:
Once
we freeze our account structure in the Key Flexfield Segments window
and begin using account numbers in data entry, we should not modify the
flexfield definition. Changing the existing flexfield structure after
flexfield data has been created can cause serious data inconsistencies.
Modifying your existing structures may also adversely affect the
behavior of cross–validation rules and shorthand aliases.
Caution 2:
Once
you are done entering the segment information, click on flexfield
qualifier and designate one of your segments as the natural account
segment and another as the balancing segment. You can optionally
designate a cost center segment and/or intercompany segment. This is the most important step.
Navigation: General Ledger Super User Responsibility
Setup à Financials à
3: Entering Segment Values
We
enter segment values which is valid for our application or
organization. The valid value can be a phrase, word, abbreviation or
numeric code. The valid value must conform to the criteria defined for
the respective valid set.
Caution :
If
you plan on defining summary accounts or reporting hierarchies, you
must define parent values as well as child or detail values.
You can set up hierarchy structures for your segment values. Define parent values that include child values. You can view a segment value’s hierarchy structure as well as move the child ranges from one parent value to another.
You can set up hierarchy structures for your segment values. Define parent values that include child values. You can view a segment value’s hierarchy structure as well as move the child ranges from one parent value to another.
Navigation: General Ledger Super User Responsibility
Setup à Financials à
4. Entering Account Combinations
This step is optional. Account combinations are part of Journal Transactions.
We
can manually enter the new account combinations in a chart of accounts
of a company using GL Accounts form. Anyhow, if we have checked the
“Allow dynamic inserts” check box in segments for then we don’t need to
worry about this step.
Navigation: General Ledger Super User Responsibility
Setup à Account à Combinations
5. Creation of Account Alias:
This step is again optional. For
input or Retrieve data about a transaction in Oracle General Ledger
requires the complete Account Combination. But generally the account
combination is large and very difficult to remember. Hence we define a
short name (Alias) for the Account combination which we use widely.
Detail Explanation of this step is available in another article. Please click the below link
6. Define Flexfield Security Rules
This step
is to prevent group of users from accessing specific segment values
while data entry and in report parameters. This maintains the integrity
of accounting data. The flexfield security rule is effective only when
assigned to an appropriate responsibility.
However to restrict all the users from accessing the particular segment value we need to disable them in segment s form.
Navigation: General Ledger Super User Responsibility
Setup à Financials à
7. Define Cross Validation Rules
This
step is required to maintain a consistent and valid set of account
combination based on our business requirements. Cross validation rule
prevent users from entering invalid account combinations. Cross
validation rules validate only new account combinations hence it needs
to be implemented before entering the chart of accounts.
Navigation: General Ledger Super User Responsibility
Setup à Financials à
Part1 of this Post contains the below,
- Definition of Chart of Accounts
- Overview
- Graphical Representation






No comments:
Post a Comment