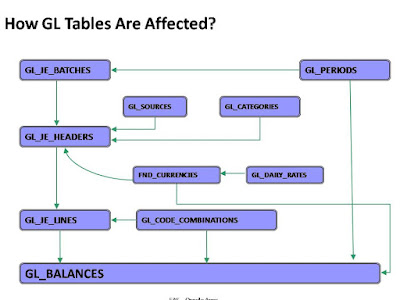
HOW GL TABLES ARE EFFECTED
GL Lession
Maintenance and Relevant ReportsCalendar Maintenance:
GL Can't be started without defining the first open period from the Open/Close Calendar option. One has to be very careful when selecting the first period as once opened a period prior to that can't be opened. Once opened, on an ongoing basis periods have to be opened and closed. New Years whould be required to be appended to the existing calendars.
Account Values Maintenance:
On a regular basis lot of values would have to be opened, disabled etc.
Use Mass Maintenance to move balances by period from one account to another or merge balances by period from multiple accounts into a single account. The moved/merged balances are added to the existing balances in your target accounts. To change a move/merge, one can reverse it and restore account balances to their previous amounts.
During a move/merge operation the financial integrity between GL and its sub ledgers is maintained.
Document Sequencing:Every time the validity of the Document sequence is over, define and assign new sequence.
Currency Rate Maintenance
Standard Reports:
Account Analysis, Trial Balance (Detailed, Summary, Expanded), Budget Reports, Chart of Accounts Reports and
Listings, Currency Listings Reports, FSG Reports on Row/Column Set Details, GL Report, Journal Reports and
Execution Reports.
Closing Procedure:
Set the status of the first accounting period in the new fiscal year to Future Entry.
If the business rules require reversing entries at the beginning of every period, generate and post accruals from the prior period. If prior period reversals were not generated and posted at the beginning of this period, then generate reversals
Transfer data from all of sub ledgers and feeder systems to the GL_INTERFACE table. Review and Post the imported journal entries. Close the period for each sub ledger. This prevents future sub ledger transactions from being posted to GL in the same period. Perform reconciliations of subsidiary ledgers by reviewing and correcting balances.
Generate all recurring journals and step–down allocations.
Revalue balances to update foreign currency journals to functional currency equivalents.
Post all journal entries, including: manual, recurring, step–down allocations, and reversals.
Update any unpostable journal entries and then post them again.
Run GL reports, such as the Trial Balance reports, Account Analysis reports, and Journal reports.
Translate balances to any defined currency if report in foreign currencies is required.
Consolidate subsidiary SOBs in case of multiple companies.
If using a calendar with an adjusting period that represent the last day of the fiscal year, close the current period and open the adjusting period. Create and post adjusting entries and accruals in the adjusting period.
Run Trial Balance reports and other GL Reports in the adjusting period after adjustments are made.
If it is required to have an actual closing journal entry that shows the closing of income statement accounts to retained earnings, submit the Create Income Statements Closing Journals program. This program creates an auditable closing journal entry. The income statement will reflect zero balances on posting
If local accounting rules require balance sheet to be closed, submit the Create Balance Sheet Closing Journals program. Balance sheet will now reflect zero balances on posting.
Close the last period of the fiscal year and Open the first period of the new fiscal year to launch a concurrent process to update account balances. Opening the first period of a new year
automatically closes income statement and posts the difference to retained earnings account specified in the SOB form.
Perform Year–End Encumbrance Procedures (if applicable).
Run FSG reports for the last period of the year.
If balance sheet is closed at year–end, reverse the Balance Sheet Closing Journals to repopulate balances of balance sheet accounts for the new year.
No comments:
Post a Comment